Facial Recognition: Exploring the Potential of Emotional Recognition
I. Introduction
Driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), facial recognition technology has surged to prominence, revolutionizing various sectors. Its potential extends beyond mere face identification, offering the tantalizing prospect of deciphering human emotions from facial expressions. This burgeoning field of emotion recognition through facial expressions unlocks a myriad of possibilities in fields ranging from security to healthcare.
II. Basic Principles of Facial Recognition
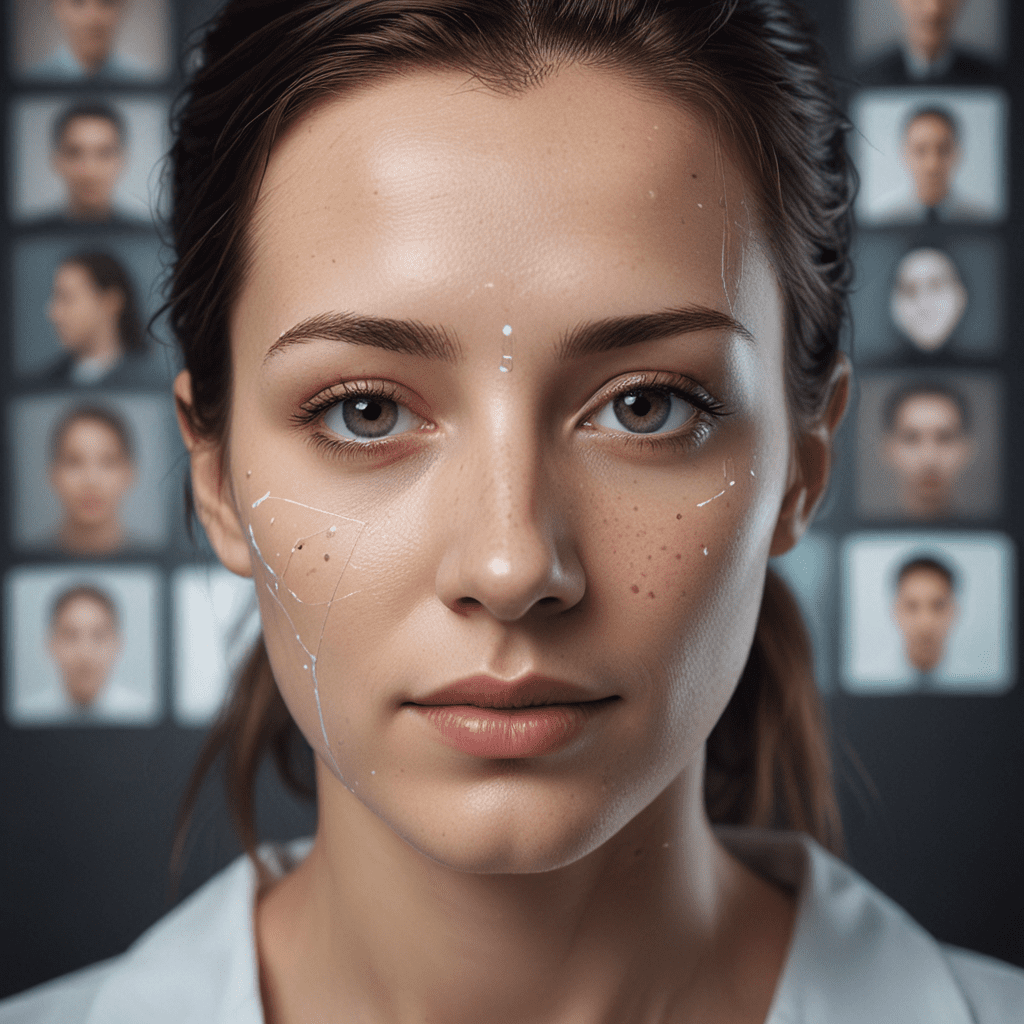
Facial recognition systems leverage sophisticated algorithms to map and analyze distinct facial features. These systems utilize machine learning techniques to extract unique identifiers, such as the shape of the eyes, nose, and mouth. By comparing these extracted features to a database of known faces, facial recognition systems can accurately identify individuals with remarkable efficiency.
III. Emotion Recognition through Facial Expressions
Facial expressions constitute a quintessential aspect of human communication, conveying emotions and intentions. Researchers have identified a set of universal facial expressions associated with core emotions, including happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust. Advanced facial recognition systems exploit this knowledge to interpret emotions by detecting subtle changes in facial muscle movements.
IV. Applications of Emotion Recognition
The advent of emotion recognition through facial expressions opens up a plethora of practical applications:
A. Security and Surveillance
Emotion recognition enhances security systems by enabling the detection of suspicious behavior based on facial expressions. For instance, at airports or border crossings, facial recognition systems can flag individuals exhibiting signs of stress or anxiety.
B. Human-Computer Interaction
Emotion recognition empowers computers with the ability to perceive and respond to human emotions. In customer service chatbots or educational software, this technology can adapt its responses based on the user's emotional state, improving user engagement and satisfaction.
C. Clinical and Healthcare
Emotion recognition has far-reaching implications in healthcare. By analyzing facial expressions, medical practitioners can assess patients' emotional well-being and detect early signs of mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety. In pain management, emotion recognition can assist clinicians in evaluating pain intensity and guiding appropriate treatment.
V. Challenges in Emotion Recognition
Despite significant advancements, emotion recognition through facial expressions faces several challenges:
A. Cross-Cultural Variations
Facial expressions can vary across cultures, potentially impacting the accuracy of emotion recognition systems. For instance, the expression of happiness may differ between Eastern and Western cultures.
B. Contextual Factors
Emotions are often influenced by contextual factors, such as social interactions, past experiences, and cultural norms. Emotion recognition systems need to account for these complexities to make accurate interpretations.
VI. Ethical Implications
The widespread deployment of emotion recognition technology raises ethical concerns. Privacy advocates express apprehension about the potential misuse of such technology for surveillance and behavior profiling. Transparent regulations and responsible usage are crucial to safeguard individuals' rights.
VII. Future Research Directions
Continued research in emotion recognition aims to address current limitations and explore new applications. Future directions include:
Developing cross-cultural emotion recognition models to cater to diverse populations.
Incorporating contextual information to enhance accuracy.
Addressing ethical implications and developing robust privacy-preserving measures.
VIII. Conclusion
Facial recognition technology, with its ability to recognize emotions, has the potential to revolutionize various industries. From enhancing security to improving healthcare outcomes, this technology offers a myriad of benefits. However, challenges remain in addressing cross-cultural variations, contextual factors, and ethical implications. Ongoing research and informed policymaking will ensure the responsible and impactful deployment of emotion recognition technology.
FAQ
What are the main emotions that can be recognized through facial expressions?
Facial recognition systems can recognize a range of universal emotions, including happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust.
How are emotions detected through facial expressions?
Advanced systems utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze subtle changes in facial muscle movements and map these movements to specific emotions.
What are the potential applications of emotion recognition?
Emotion recognition has wide-ranging applications in security, human-computer interaction, healthcare, and various other fields.