Understanding Geothermal Power Plant Operations
Geothermal energy is a sustainable and renewable source of power that harnesses the heat from beneath the Earth’s surface. Geothermal power plants play a crucial role in converting this heat into electricity efficiently. Let’s delve into the operations of geothermal power plants to understand how this clean energy is produced.
The Geothermal Resource:
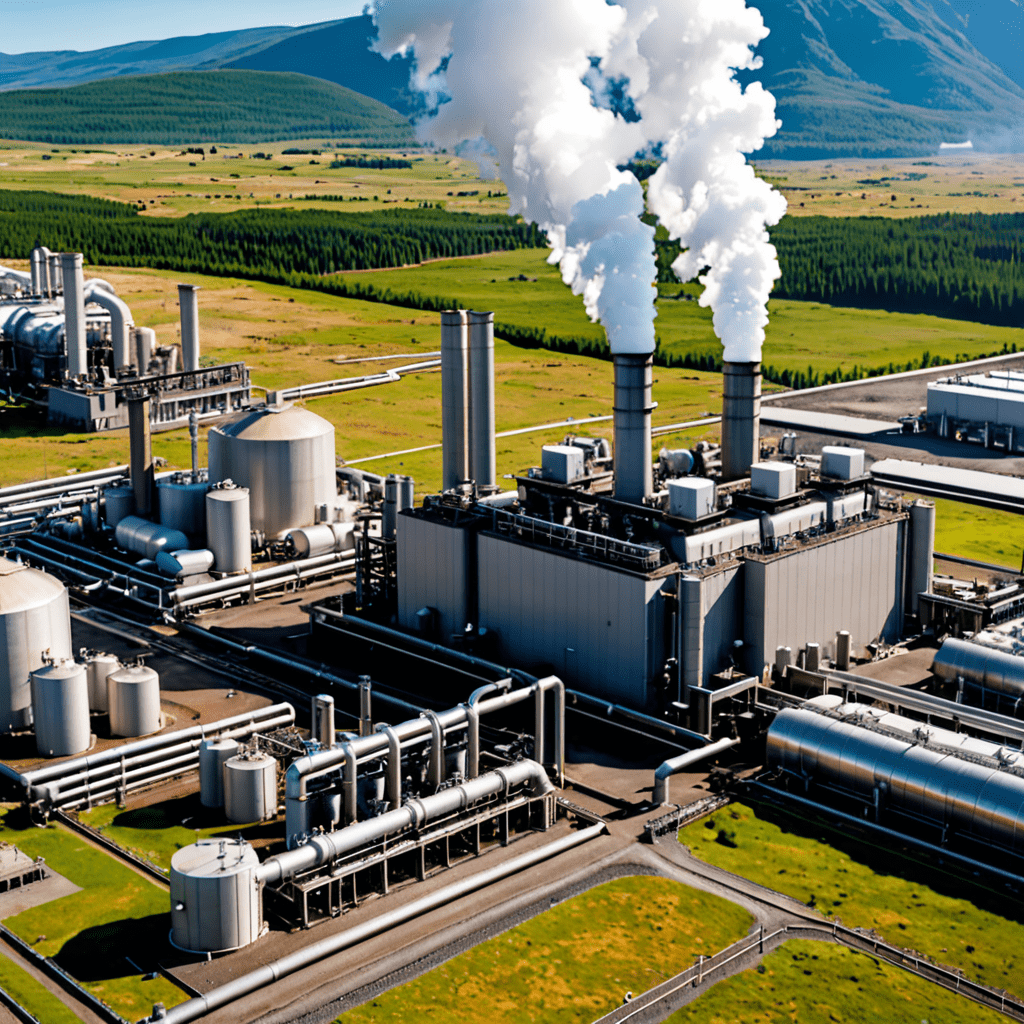
Geothermal power plants utilize the Earth’s natural heat, which originates from molten rock beneath the surface. This heat is accessed through wells drilled deep into the Earth to reach the reservoirs of hot water and steam.
Fluid Circulation System:
Once the hot water or steam is extracted from the reservoir, it flows through a piping system to the surface. This fluid circulation system carries the geothermal energy to the power plant for electricity generation.
Energy Conversion:
At the power plant, the geothermal fluid is passed through a heat exchanger, where its heat is transferred to a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point, such as isobutane or pentane. This process converts the geothermal energy into mechanical energy.
Turbine and Generator:
The mechanical energy drives a turbine connected to a generator. As the turbine spins, it generates electricity through the movement of magnets within the generator. This electricity is then ready for transmission to the grid.
Reinjection:
After the geothermal fluid has passed through the heat exchanger, it loses some of its heat and is re-injected into the Earth’s reservoir. This reinjection process ensures sustainability by maintaining the pressure and heat levels of the geothermal resource.
Environmental Impact:
Geothermal power is a clean energy source with minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. It produces low levels of greenhouse gas emissions and does not rely on fuel combustion, making it a sustainable option for electricity generation.
Future of Geothermal Energy:
As advancements continue in geothermal technology, the efficiency and capacity of geothermal power plants are expected to increase. With a greater focus on renewable energy sources, geothermal energy is poised to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable and greener energy future.
FAQs About Geothermal Power Plant Operations
What is geothermal energy and how is it used in power plants?
Geothermal energy is heat from the Earth’s core stored in rocks and fluids beneath the Earth’s crust. Geothermal power plants use this heat to generate electricity by tapping into hot underground reservoirs, converting the steam and hot water into power.
What are the main types of geothermal power plants?
There are three main types: dry steam plants, flash steam plants, and binary cycle plants. Dry steam plants draw steam from underground wells to run turbines, whereas flash steam plants use high-pressure hot water from wells to create steam. Binary cycle plants transfer heat from geothermal water to another fluid with a lower boiling point to generate steam and drive turbines.
How do geothermal power plants affect the environment?
Geothermal power plants have minimal environmental impact compared to fossil fuel plants. They produce lower emissions and don’t rely on burning fuels, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, there are concerns about water usage and potential for inducing seismic activity in certain cases.
What are the advantages of geothermal power plants?
Geothermal power plants provide renewable, reliable, and sustainable energy. They have a small land footprint, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and offer continuous power generation regardless of weather conditions. Additionally, geothermal energy is cost-effective and helps