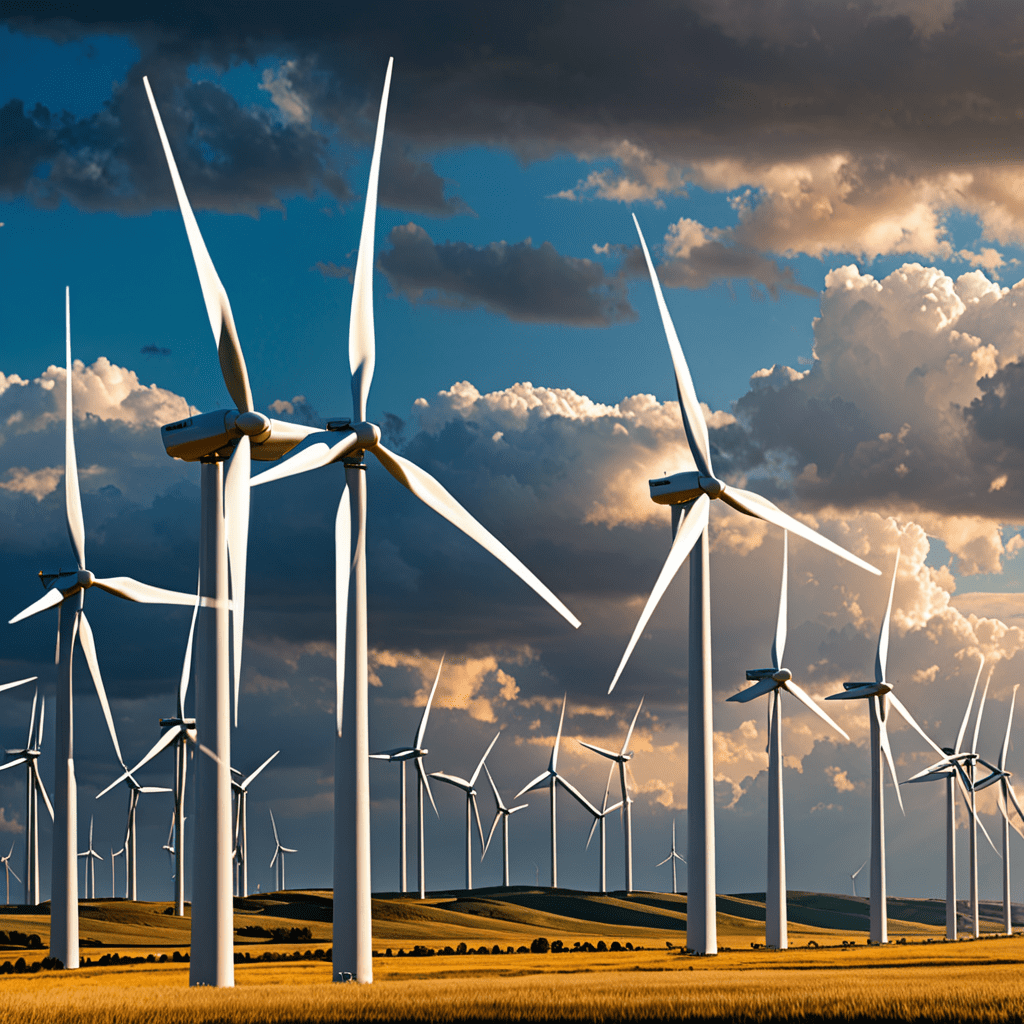
Exploring the Future of Wind Energy: Innovations in Turbine Design
The Evolution of Wind Turbines
Wind energy has seen remarkable advancements in turbine technology over the years. From traditional horizontal axis turbines to vertical axis and beyond, the design innovations have revolutionized the efficiency and effectiveness of harnessing wind power.
Smart Blade Technology
One of the cutting-edge innovations in turbine design is the integration of smart blade technology. These blades are equipped with sensors and actuators that allow them to adjust their angles in real-time, optimizing energy capture in varying wind conditions.
Offshore Floating Turbines
Offshore wind farms are becoming increasingly popular, and the development of floating turbines has opened up new possibilities for harnessing wind energy in deeper waters. These innovative designs offer greater flexibility in turbine placement and can potentially generate more power than traditional fixed-bottom turbines.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT)
Vertical axis turbines have gained attention for their unique design that allows them to capture wind from any direction without the need for complex yaw mechanisms. VAWTs are particularly suitable for urban environments and can be integrated into buildings to harness wind energy efficiently.
Hybrid Turbines
Hybrid turbines combine different technologies, such as solar panels or energy storage systems, with traditional wind turbines to create integrated renewable energy solutions. These innovative designs maximize energy production and grid stability while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Bladeless Wind Turbines
Bladeless wind turbines offer a radically different approach to traditional designs by utilizing oscillating structures to capture wind energy. These innovative turbines have the potential to reduce noise pollution and minimize bird and bat collisions, addressing some common concerns associated with conventional wind turbines.
The Future of Wind Turbine Design
As technology continues to evolve, the future of wind turbine design holds immense promise. Advancements in materials science, aerodynamics, and artificial intelligence are driving the development of more efficient, reliable, and sustainable wind energy solutions. By embracing innovation and pushing the boundaries of conventional design, we can unlock the full potential of wind energy as a clean and renewable power source for the future.
FAQ About Wind Energy Innovations in Turbine Design
What are some recent innovations in wind turbine design?
Recent innovations in wind turbine design include advancements in aerodynamics, materials, and control systems. Manufacturers are constantly improving blade design to increase energy capture and efficiency while reducing noise. Smart technologies like sensors and data analytics are being integrated to optimize performance and maintenance scheduling.
How do vertical axis wind turbines differ from traditional horizontal axis turbines?
Vertical axis wind turbines have their rotor shaft positioned vertically, unlike horizontal axis turbines where the shaft is horizontal. Vertical axis turbines can potentially have lower production costs, easier maintenance, and the ability to generate power from varying wind directions. However, horizontal axis turbines are more common and have higher efficiency levels.
Can offshore wind turbine designs significantly impact renewable energy production?
Offshore wind turbine designs have the potential to significantly impact renewable energy production. Offshore turbines can capture stronger and more consistent wind speeds than onshore ones, leading to higher energy output. Floating turbine designs are being developed for deeper waters, opening up more locations for wind energy production.
How do bladeless wind turbines work and what are their advantages?
Bladeless wind turbines utilize oscillating poles to capture wind energy. These turbines produce less noise, have lower maintenance needs, and pose less harm to wildlife compared to traditional bladed turbines. The design also allows for placement in urban